Dental surgery extends far beyond tooth extraction. The field embraces a wide range of procedures performed within the mouth, including the procedures that support other branches of dentistry, e.g. implantology, prosthodontics and periodontology.
Extraction of impacted teeth – The term refers to the fully developed teeth which nevertheless do not erupt through the gum, and as a result are blocked in the bone tissue of either the mandible or the maxilla.
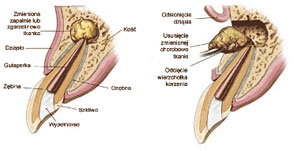
Apicoectomy – Dental surgery that involves the resection of a root’s apex, and the methodic removal of any damage in the periodontium, which may occur as a result of unsuccessful endodontic therapy or develop as tooth pulp disorder complication. The bone hollow is subsequently filled with biocompatible materials that stimulate bone recreation processes and healing. Over the course of several months, the bone heals around the root, restoring full function.
Hemisection - Involves the separation of a root from the crown of a tooth with two roots.
Alveolar process plastic surgery - The term refers to a wide range of preliminary procedures performed on both soft and hard tissues of the mouth, which prepare a patient to undergo a planned prosthetic therapy in cases of considerable irregularities of the alveolar process intended to support a denture.
Single and multiple tooth extractions
Surgical therapy of periodontal diseases - Regenerative therapy of periodontal tissues, applied in surgical practice thanks to the implementation of the right substances and operative techniques. These procedures are also referred to as guided tissue and bone regeneration. They include gingival grafting and transplantation, heterogeneous and autogenous bone grafting, gingival flap surgeries with the use of barrier membranes and free gingival autografts in root coverage.
Guided bone regeneration - The procedure is often performed prior to placement of dental implants, to support tissue growth and assure implant stability in cases of severe bone loss resulting from periodontitis.
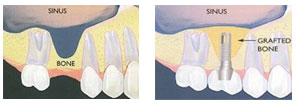
Sinus lift - Also referred to as maxillary sinus floor augmentation procedure, is performed in order to increase the amount of bone in the posterior maxilla, or upper jaw bone prior to placement of an implant. Sinus lifting stimulates bone tissue growth. The procedure employs the mechanisms of guided bone regeneration. Barrier membranes or bone grafts are grown into defective areas, which – due to natural regenerative processes – are rebuilt by the patient’s own bone tissue in the course of several months.
Frenuloplasty - Involves the alteration of ill-developed frenula of the upper lip, tongue and cheeks. There may be periodontological, orthodontic (e.g. when a diastem exists between fully developed permanent maxillary incisors or prior to the introduction of braces), and prosthodontic (ill-developed frenula may destabilize removable dentures) indications.
Crown lengthening - The procedure is aimed at altering the gingival tissue so as to expose the crown fractures or decay extending below the gingival margin. As a result, after the healing process is completed, prosthetic procedures may be performed or the shape of the crown may be altered to suit the shape of the adjacent teeth.
Closure of oroantral connection - Sometimes the extraction of maxillary molars cause the creation of oroantral connections. the reason why this happens is that root apices of molar teeth are situated in the maxillary sinus. In cases when the sinus is perforated by an apex, a surgery must be performed. It involves the closing of the gap. Otherwise, neglection may lead to acute sinusitis which can in turn require hospitalization and more complicated surgical procedures.